An ancient tooth found in a cave has been linked to the Denisovans, a sister species of modern humans. The tooth was first found during an archaeological survey in a remote area of Laos. Now, scientists have shown that it originated from the same ancient human species that was first discovered in Denisova Cave in the mountains of Siberia.
The Denisovans are believed to be cousins of the Neanderthals, which are often pictured like the man in the image above. Now that scientists have connected this tooth to the species, many believe it can unlock some of the mystery surrounding these ancient humans.
This ancient tooth could unlock the mystery of an ancient sister species of modern humans
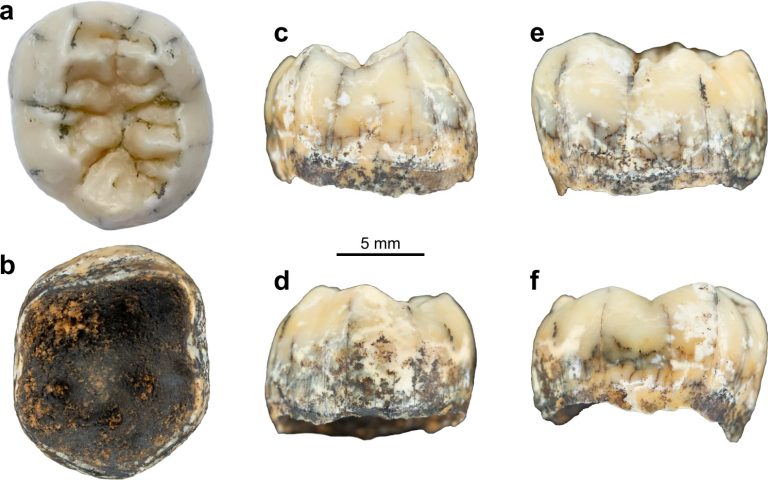
Image source: Fabrice Demeter, et al / Nature Communications
The ancient tooth was found during a 2018 excavation in northern Laos. The cave in question, known as Tam Ngu Hao 2, or Cobra Cave, is close to another important archaeological find at Tam Pà Ling Cave. Previously, scientists discovered 70,000-year-old human fossils in Tam Pà Ling Cave.
Despite being thousands of miles apart, an international group of scientists believes that the finds are linked. Thus, the ancient tooth and fossils found in Denisova Cave belong to the same species of ancient humans. The group published a study on their findings in Nature Communications.
The ancient tooth, Professor Fabrice Demeter, lead author on the study, shows that the Denisovans were active in Southeast Asia, at least as far as Laos. The scientists studied the shape of the tooth, which they said shares many similarities with Denisovan teeth found on the Tibetan Plateau. That’s the only other location where we’ve found Denisovan fossils.
Based on these discoveries, they believe that Denisovans lived between 164,000 and 131,000 years ago. Scientists also believe they lived in the warm tropical areas that make up northern Laos. Some have even referred to the ancient tooth as a “smoking gun” in the search for more evidence of the Denisovans. (via SciTechDaily)
Who were the Denisovans?
But what do we know about the species that this ancient tooth supposedly belongs to? Well, not much, as it turns out. Scientists previously found a dragon-man skull that they believed could be linked to the Denisovan people. Overall, though, information about this species is light. The Denisovans, or Denisova hominins, are believed to be an extinct species or subspecies of ancient humans.
Scientists believe the ancient people lived throughout Asia during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic periods. However, remains of the Denisovans have been hard to come by. In fact, we have uncovered very few physical remains as of yet. Most of what we know of this species we discovered by analyzing DNA evidence.
As such, science hasn’t given the species an official name just yet. We identified the first Denisovan individual back in 2010. DNA from a finger bone uncovered in the Altai Mountains in 2008 exposed the first evidence of this ancient species. Following that first discovery, additional finds, such as the ancient tooth, have helped scientists learn more about the Denisovan people.
Still, there’s a lot we don’t know about these people. But, with this ancient tooth now linked to the species, we at least have a better idea of when they were around. As well as where they lived during those time periods. Perhaps the ancient tooth can even teach us more as scientists continue to analyze it.








