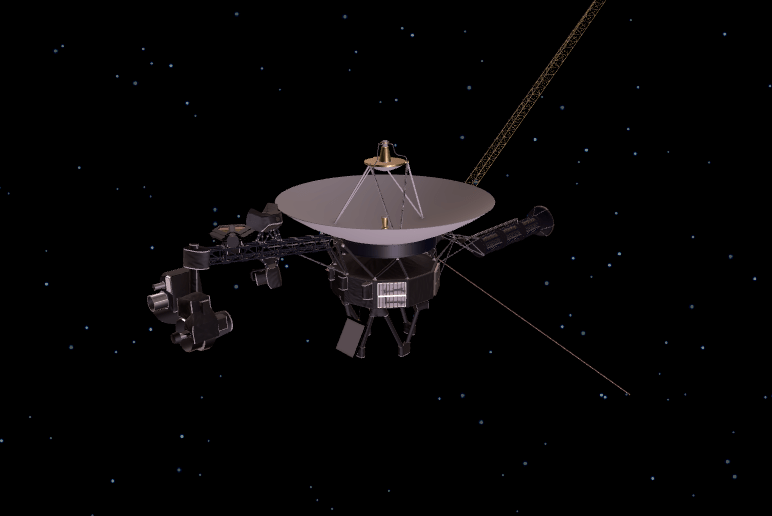
NASA hardware tends to last a long time, but few spacecraft can match the longevity of the two Voyager probes. The twin spacecrafts were launched way back in 1977, and now NASA has revealed that Voyager-2 just achieved a milestone that only its sister ship has accomplished before it: entering interstellar space.
Voyager-2’s transition to interstellar space — meaning that it’s completely left our solar system and broken free of the “bubble” created by our star — has obviously been a long time coming. It’s been cruising through space for over 41 years and traveled an incredible 18.5 billion miles in that time. Now it joins its sister in an adventure into the great unknown.
Voyager-2 (which was actually launched before Voyager-1 by about two weeks), traveled a bit slower than its peer. Voyager-2 has been traveling at 34,390 miles per hour while Voyager-1 outpaces it at just over 38,000 mph. That slower speed allowed Voyager-1 to overtake the spacecraft that launched before it and reach interstellar space between late 2012 and early 2013.
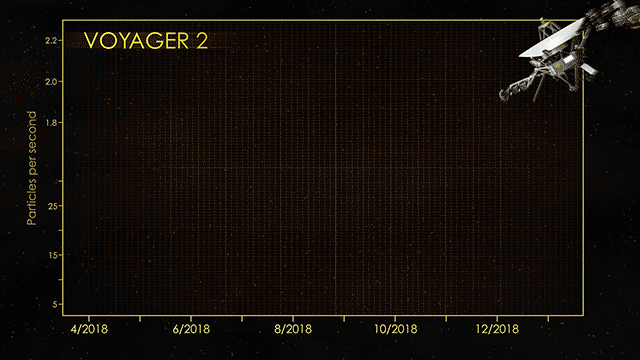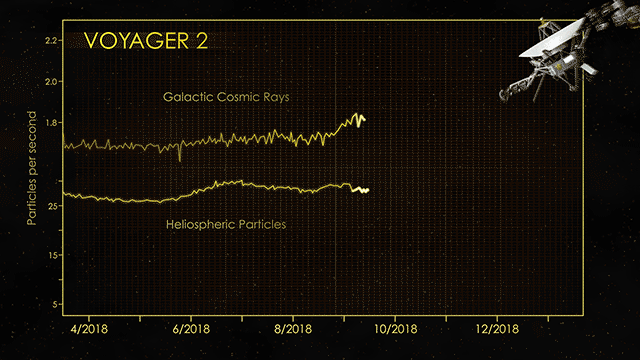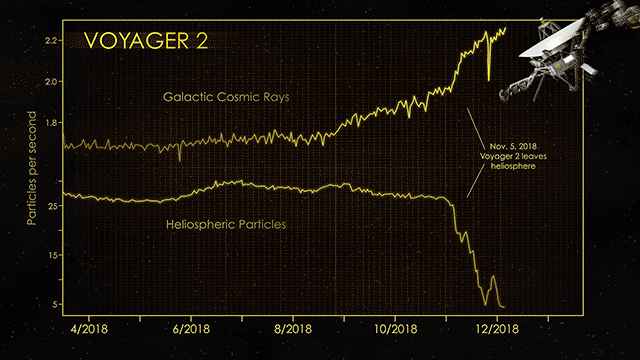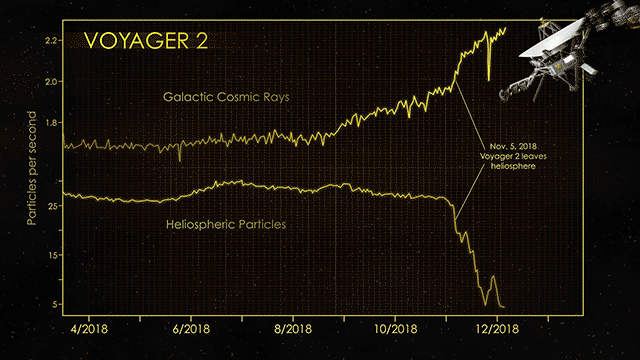
Determining exactly when a spacecraft leaves the solar system and officially enters interstellar space is surprisingly difficult. As NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory explains, engineers have to compare the readings of various spacecraft instruments that detect particles generated by the Sun as well as cosmic rays. As cosmic ray readings spike upwards and detection of solar particles drops off, the team makes the call that the spacecraft officially left the system.
“Voyager has a very special place for us in our heliophysics fleet,” NASA’s Nicola Fox said in a statement. “Our studies start at the Sun and extend out to everything the solar wind touches. To have the Voyagers sending back information about the edge of the Sun’s influence gives us an unprecedented glimpse of truly uncharted territory.”
But what’s next for the two Voyagers? Nobody really knows. The two probes were designed to cruise endlessly through space and, if they’re ever found, they’ll give extraterrestrials a small taste of Earth.