ChatGPT Just Got Mind-Blowing Computer Vision Powers Like In The Movies
OpenAI surprised us all with ChatGPT's new image-generation features, which went viral a few weeks ago. However, it's worth remembering that the chatbot doesn't just create images from a text prompt; it can also understand pictures. ChatGPT got its multimodal capabilities last May, which include the ability to look at files, including images.
Fast-forward to OpenAI's o3 and o4-mini announcement earlier this week, and ChatGPT got a massive upgrade concerning images. It's something that easily tops its ability to create celebrity deepfakes or Studio Ghibli-style photos.
ChatGPT's new reasoning models (o3 and o4-mini) can look at an image and integrate it into their chain of thought when handling a question or prompt. The AI manipulates images on its own, which means it can rotate, crop, and zoom in on a photo to find the information you're looking for.
This is the closest thing we have to the computer vision we see all the time in movies. You know, when the star of the film or TV show tells the tech guy to enhance a blurry image, and then the computer makes everything crystal clear. That can't happen in real life (well, it sort of can), but AI like ChatGPT o3 and o4-mini can now understand images and their contents much better than before. They can make sense of blurry details in images, just like the computers in those movies.
As a ChatGPT Plus user, I already got access to o3 and o4-mini, which is surprising, considering I live in Europe. I haven't had a chance to try the new visual reasoning feature, but I went through OpenAI's demos, and they blew my mind. Here are a few of them:
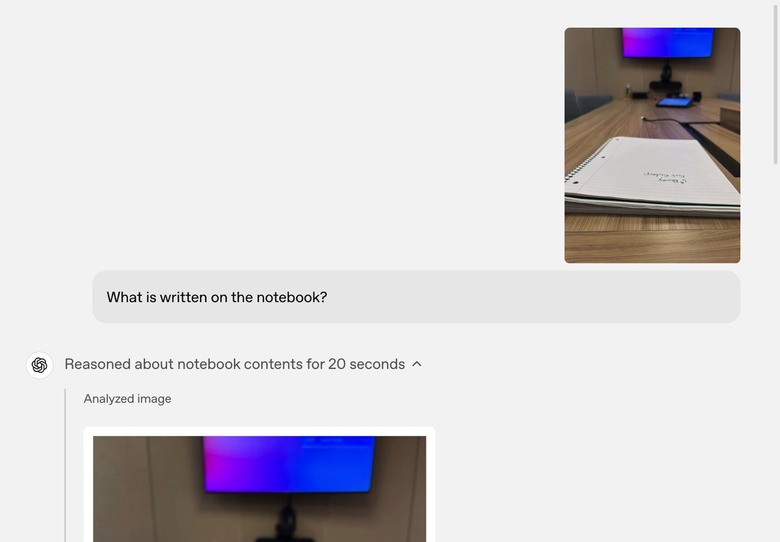
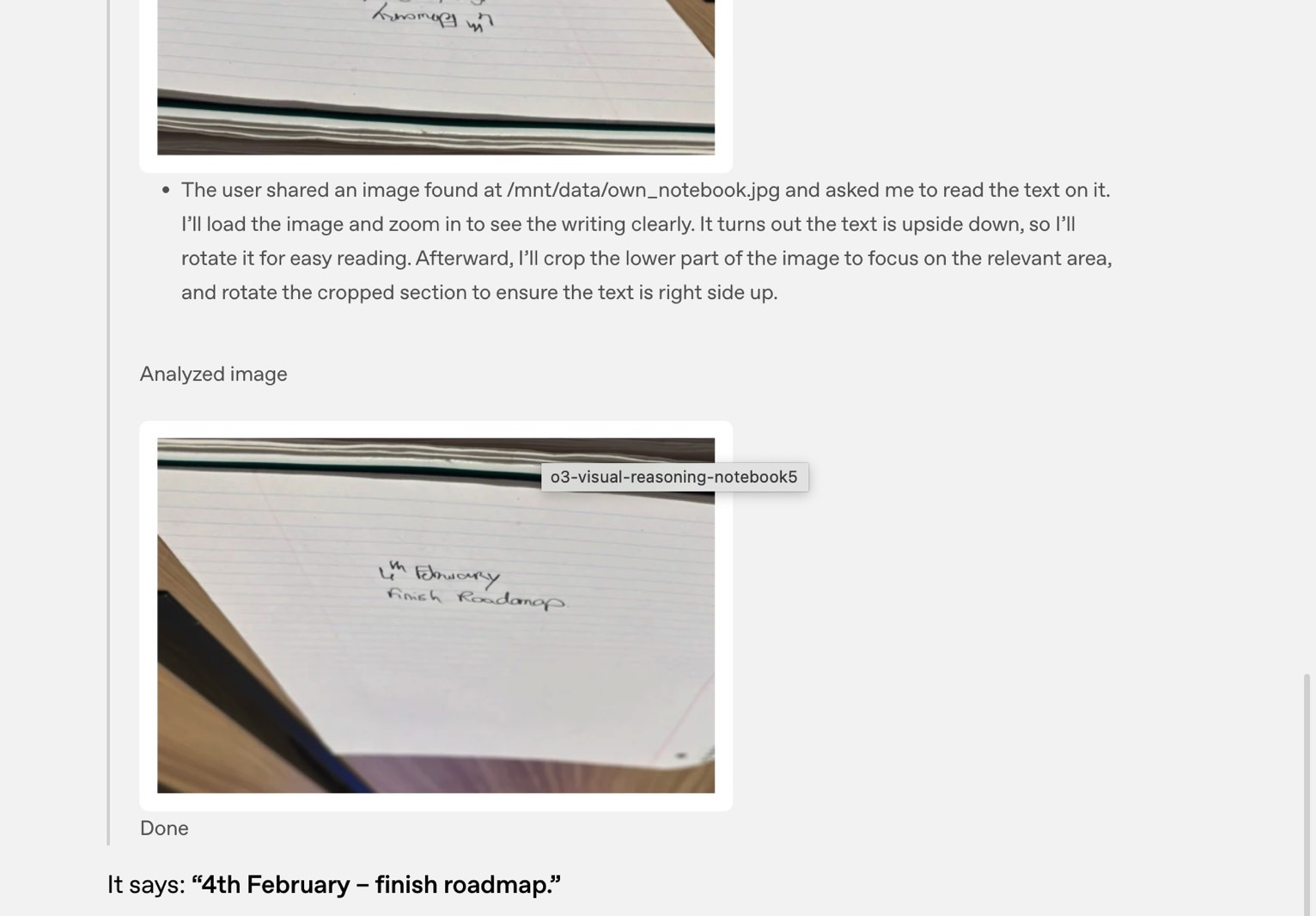
What is written on the notebook?
In this prompt, OpenAI uploaded a photo of a notebook to ChatGPT o3, asking it "What is written on the notebook?"
The AI looked at the image, flipped it, recognized the handwriting, and produced the answer.
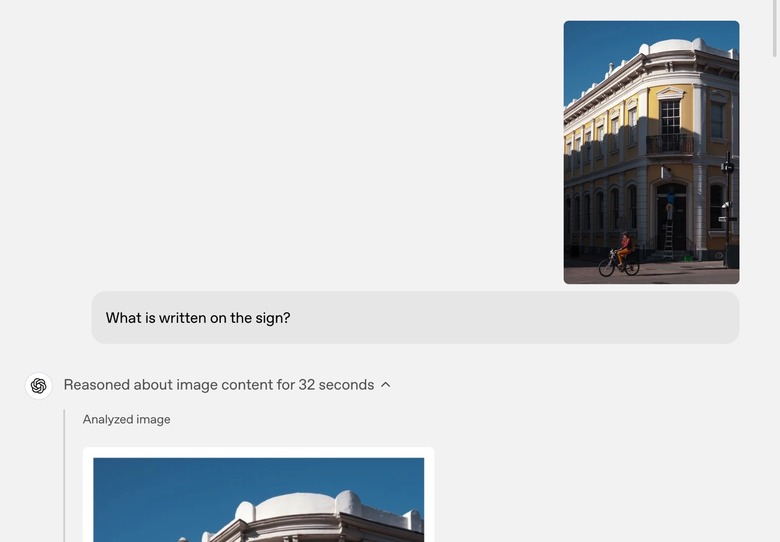
What is written on the sign?
When I saw the following image, I immediately asked, "What sign???"
Then, I saw ChatGPT zooming in to find the answer, which it did. Yes, I guess the AI can read blurry images that contain text. Earnestly, I could have made that text up myself after enough zooming. But it'll be even faster if the AI can pick it up.

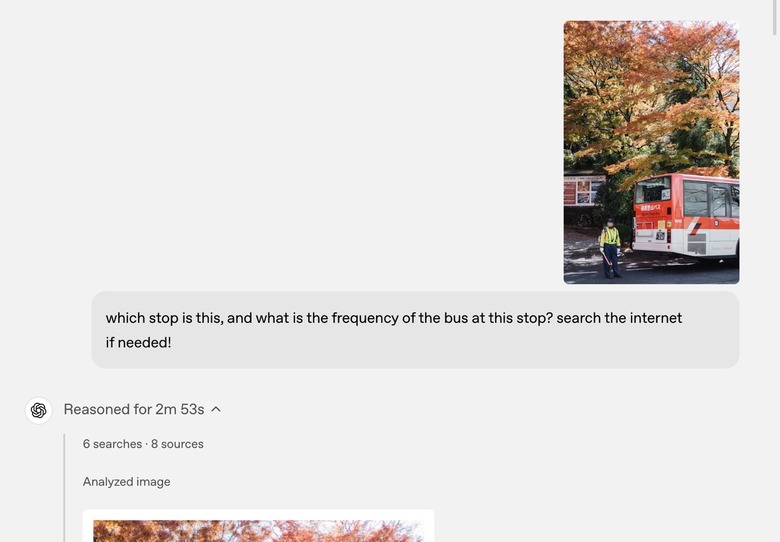
Which stop is this?
ChatGPT o3 had to do more than zoom into a photo to answer this prompt: "which stop is this, and what is the frequency of the bus at this stop? search the internet if needed!"
The AI had to determine the location, read some of the text visible on the sign, and then provide a final answer.
ChatGPT o3 had no problem reasoning through it, even though it needed nearly three minutes to answer the question.

The AI determined the location, zoomed in on the board in the background, translated the text, and then provided a response. Mind. Blown.

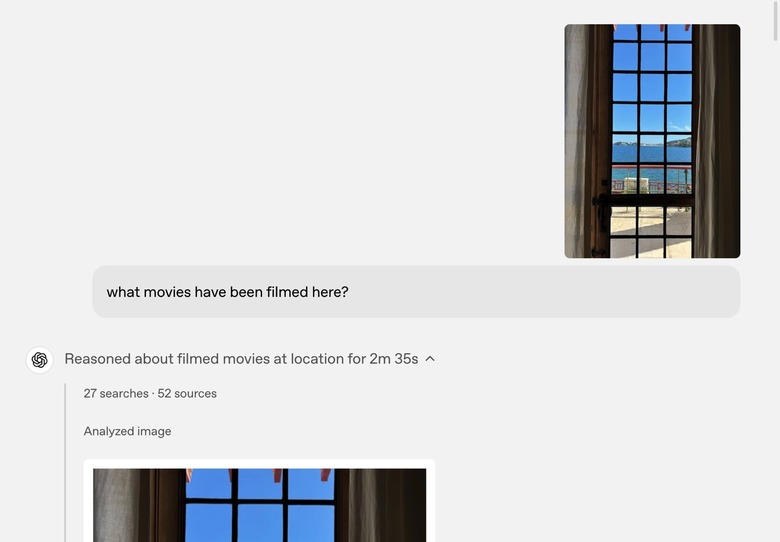
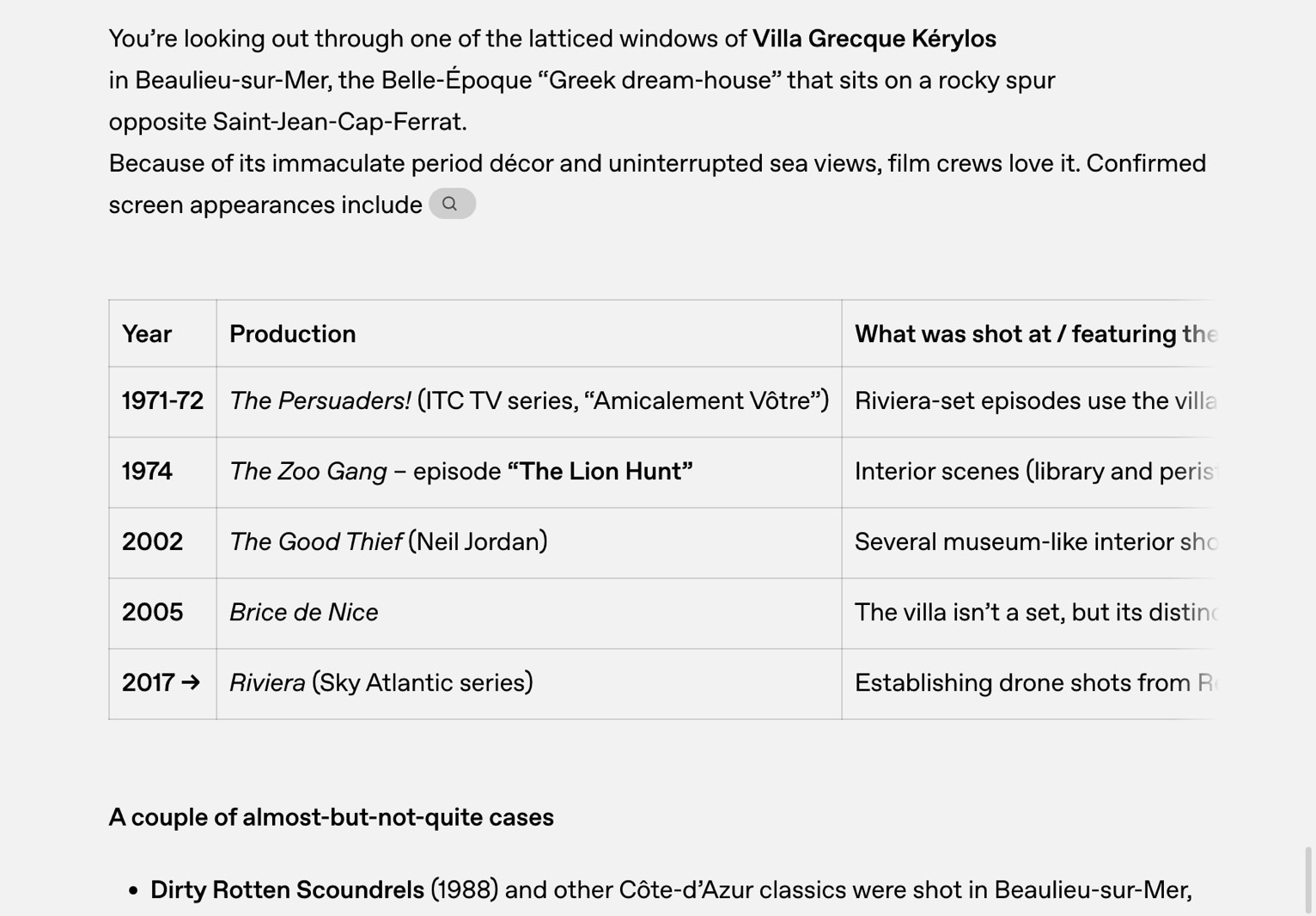
What movies have been filmed here?
Equally impressive is the following demo that OpenAI offered. The AI was given a photo of a location taken through a window.
OpenAI asked ChatGPT o3 what movies were filmed at that location, a question that involves reasoning.
First, the AI needs to determine the location by looking out the window. Then, it has to find the movies that might have been shot near that location by browsing the web.
I don't expect ChatGPT's new visual reasoning to work flawlessly every time. But if the AI can handle images in its chain of thinking like these OpenAI demos suggest, then we're looking at incredible functionality for AI chatbots. And yes, the AI's visual reasoning abilities should improve significantly with future models.
You can see more ChatGPT visual reasoning examples at this link.