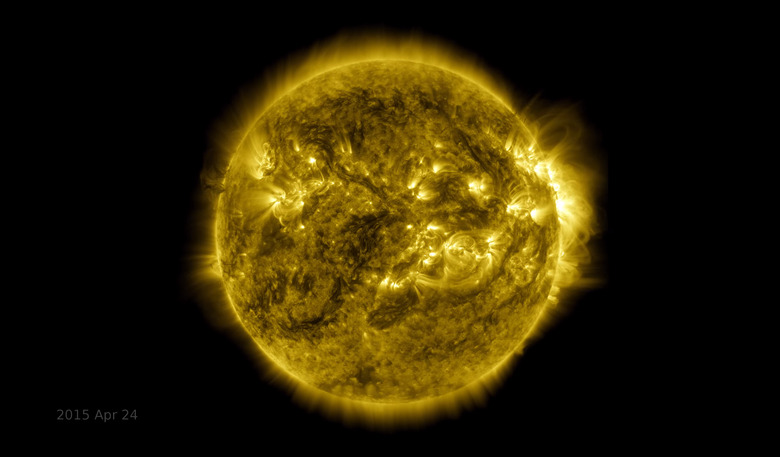
The ESA Just Snapped The First Photos Of The Sun's South Pole
The European Space Agency has achieved yet another "first" for humankind by capturing the first photos of the Sun's south pole. These images were captured by the agency's Solar Orbiter spacecraft, and it gives us our first distinct look at the atmosphere of the Sun's southern pole.
When viewed from our little blue planet, the Sun appears as nothing more than a massive disc of light. However, thanks to the efforts of the Parker Solar Probe and other astronomical observations, we know that isn't really the case. Like the other planets in our solar system, the star that it all revolves around is massive, and made up of several different regions.
Further, because the star is made up of so much pure, raw energy, it's more like a roaring ball of power, with magnetic fields twisting and turning around it as it rotates. These fields are what help determine when the Sun sends solar energy ripping through space into our solar system, and understanding them is key to understanding our Sun's potential power.
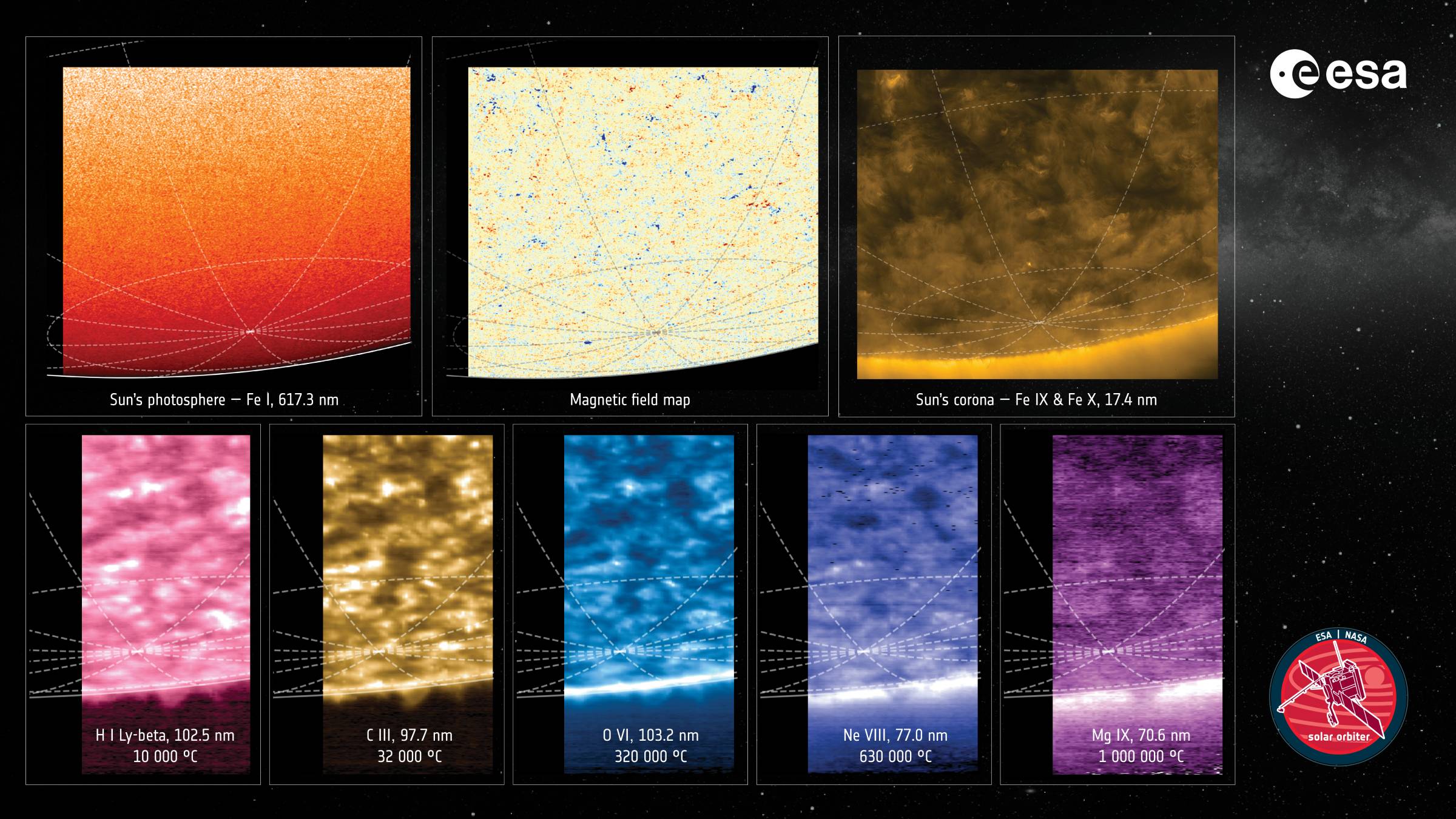
We know that our Sun goes through a relatively quiet period, where the Sun's south and north pole are clearly defined. However, there's also a time where it's less stable, and the Sun is much more violent, with energy ripping off the surface of the star more frequently. Observing this has been difficult in the past, as we had no clear indicator of where the Sun's south and north poles were.
However, that changes now, thanks to the latest observations from the ESA's Solar Orbiter. Knowing where the Sun's north and south poles are will help us follow the magnetic fields as they go through a polar reversal, which changes how the energy flows on the surface of our star.
Now, researchers believe they may actually be able to watch where the flow of power and fluid transports bits of the Sun's solar energy to the poles. The goal of this observation is to help us come up with better computer models to estimate and predict when solar outbursts will occur.
Because solar storms can be so damaging to Earth's own magnetic field, having a good idea of where and when they might strike is key to protecting future space missions. However, there's still a lot of work to do if we want to be able to predict where the solar energy will erupt from. Until then, at least we have a good foundation to build off of.
